- Order number: MIKROE-2699
- Manufacturer product ID: MIKROE-2699
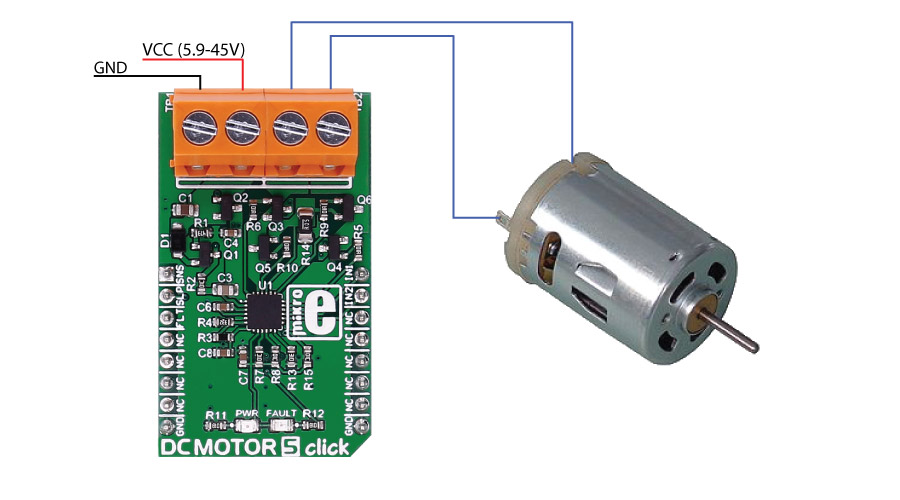
DC MOTOR 5 click carries the DRV8701 brushed DC motor gate driver from Texas Instruments. The click is designed to run on an external power supply. It communicates with the target MCU over the following pins on the mikroBUS™ line: AN, RST, CS, PWM, and INT.
DRV8701 driver features
The DRV8701 is an H-bridge gate driver (also called a pre-driver or controller). The device integrates FET gate drivers in order to control four external NMOS FETs. The device can be powered with a supply voltage between 5.9V and 45V.
Internal protection functions are provided: under-voltage lockout, charge pump faults, overcurrent shutdown, short-circuit protection, pre-driver faults, and overtemperature.
How the click works
The motor's velocity and direction can be adjusted with two PWM input signal's.
Specifications
| Type | DC |
| Applications | Industrial brushed-DC motors, robotics, home automation, etc. |
| On-board modules | DRV8701 Brushed DC Motor Full-Bridge Gate Driver |
| Key Features | supply voltage between 5.9V and 45V |
| Interface | GPIO |
| Click board size | M (42.9 x 25.4 mm) |
Pinout diagram
This table shows how the pinout on DC MOTOR 5 click corresponds to the pinout on the mikroBUS™ socket (the latter shown in the two middle columns).
Buttons and LEDs
| Designator | Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| LD1 | PWR | LED | Power Indication LED |
| TB1 | VM | CD | Voltage input connector |
| TB2 | Out_M | CD | Motor connector |
Maximum ratings
| Description | Min | Typ | Max | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply VOltage | 5.9 | 45 | V | |
| Source Current | 6 | 150 | mA | |
| Sink Current | 12.5 | 300 | mA | |
| Applied PWM signal | 100 | kHz | ||
| Operating ambient temperature | -40 | 125 | ? |
Programming
Code examples for DC MOTOR 5 click, written for MikroElektronika hardware and compilers are available on Libstock.
Code snippet
The following code snippet shows an example of DC motor 5 click usage. It will detect button press, and change the state of the control pins, putting the motor into one of the 4 possible states.
01 void main()
02 {
03 systemInit();
04
05 while (1)
06 {
07 // Coast
08 if (Button(&GPIOD_IDR, 1, 1, 1))
09 {
10 IN1_PIN = 0;
11 IN2_PIN = 0;
12 }
13
14 // Reverse
15 if (Button(&GPIOD_IDR, 2, 1, 1))
16 {
17 IN1_PIN = 0;
18 IN2_PIN = 1;
19 }
20
21 // Brake
22 if (Button(&GPIOD_IDR, 3, 1, 1))
23 {
24 IN1_PIN = 1;
25 IN2_PIN = 1;
26 }
27
28 // Forward
29 if (Button(&GPIOD_IDR, 4, 1, 1))
30 {
31 IN1_PIN = 1;
32 IN2_PIN = 0;
33 }
34
35 }
36 }








